BEIRUT (news agencies) — The prospect of a full-scale war between Israel and Lebanon’s Hezbollah militant group terrifies people on both sides of the border, but some see it as an inevitable fallout from Israel’s ongoing war against Hamas in Gaza, particularly as cease-fire negotiations have faltered.
Such a war could be the most destructive either side has ever experienced.
Israel and Hezbollah each have lessons from their last war, in 2006, a monthlong conflict that ended in a draw. They’ve also had nearly nine months to prepare for another war, even as the United States tries to prevent a widening of the conflict that could spark a confrontation with Iran and endanger U.S. forces in the region.
Here’s a look at each side’s preparedness, how war might unfold and what’s being done to prevent it.
The 2006 war, six years after Israeli forces that had occupied southern Lebanon withdrew, erupted after Hezbollah captured two Israeli soldiers and killed several others in a cross-border raid.
Israel launched a full-scale air and ground offensive and imposed a blockade that aimed to free the hostages and destroy Hezbollah’s military capabilities — a mission that ultimately failed.
Israeli bombing leveled large swaths of south Lebanon and Beirut’s southern suburbs. Hezbollah fired thousands of unguided rockets into northern Israel communities.
The conflict killed some 1,200 Lebanese, mostly civilians, and 160 Israelis, mostly soldiers.
A United Nations resolution ending the war called for withdrawal of Israeli forces from Lebanon and a demilitarized zone on Lebanon’s side of the border.
Despite the deployment of U.N. peacekeepers, Hezbollah continues to operate in the border area, while Lebanon says Israel regularly violates its airspace and continues to occupy pockets of Lebanese land.
An Israel-Hezbollah war could be “a catastrophe that goes far beyond the border, and frankly, beyond imagination,” U.N. Secretary-General Antonio Guterres warned last week, amid rising rhetoric and fears of a conflict.
Iran-backed Hezbollah initially seemed caught off-guard by Hamas’ Oct. 7 attack on Israel, a regional ally, but began firing rockets into northern Israel the following day. Since then, Hezbollah and Israel have exchanged near-daily cross-border strikes, escalating gradually. Israel also carried out targeted killings of Hezbollah and Hamas figures in Lebanon.
More than 450 people, mostly fighters with Hezbollah and allied groups but also more than 80 civilians and noncombatants, have been killed on Lebanon’s side, and 16 soldiers and 11 civilians on Israel’s.
Tens of thousands have been displaced on both sides. There are no immediate prospects for their return.
Last week, the Israeli army said it has “approved and validated” plans for an offensive in Lebanon, although the decision to launch such an operation would have to come from the country’s political leadership.
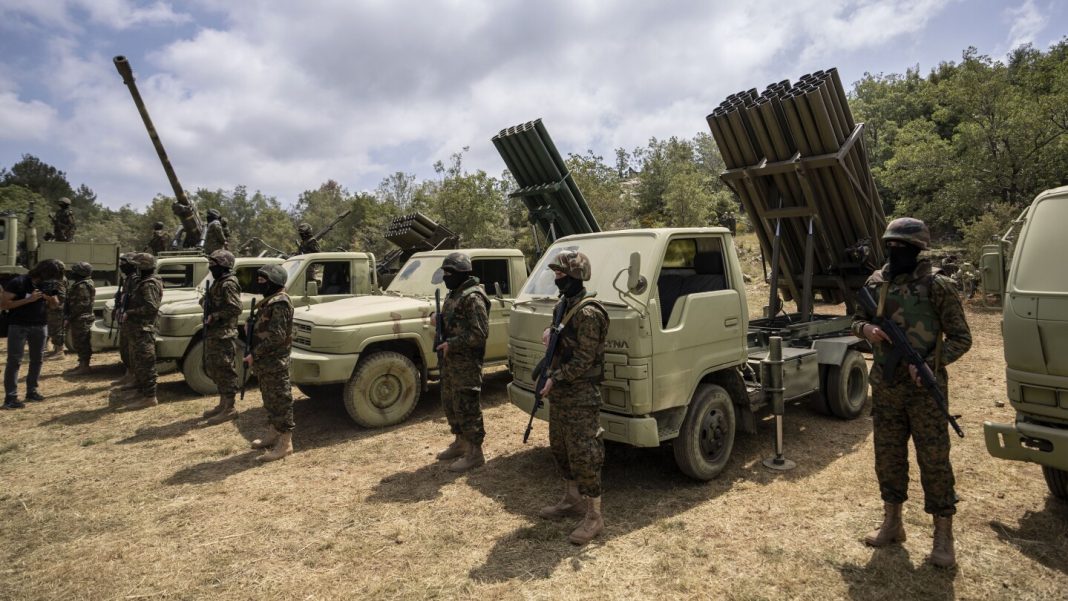
Hezbollah has released surveillance drone videos showing sites in Israel with the words “Whoever thinks of war against us will regret it.” And the group’s leader, Hassan Nasrallah, has warned of a fight “without limits” if Israel does.
Hezbollah says it won’t agree to a cease-fire on the Israel-Lebanon border before there’s one in Gaza, a prospect that looks increasingly unlikely.
Both Hezbollah and the Israeli military have expanded capabilities since 2006 — yet both countries are also more fragile.
In Lebanon, more than four years of economic crisis have crippled public institutions, including its army and electrical grid, and eroded its health system. The country hosts more than 1 million Syrian refugees.
Lebanon adopted an emergency plan for a war scenario in late October. It projected the forcible displacement of 1 million Lebanese for 45 days.